Nouvelles diverses | Page 8
actualités internationales Gouvernance Normes d'encadrement objectifs de l'entreprise Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
En rappel : Stakeholder Principles in the COVID Era
Ivan Tchotourian 31 juillet 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
Alors que les entreprises se relancent péniblement, un rappel de ces mots du Forum économique mondial d’avril 2020 paraît adéquat (histoire de ne pas oublier et de ne pas faire primer l’économique et le financier sur toute autre considération).
Déclaration « Stakeholder Principles in the COVID Era »
As business leaders, we are experiencing how profoundly the COVID-19 emergency is affecting the world. Our employees face health risks in their daily lives, and challenges in performing their jobs. Our ecosystem of suppliers and customers is under extreme pressure. By doing all we can to coordinate our work, we can ensure that our society and economy get through this crisis and we can mitigate its negative impact on all of our stakeholders.
We accept our responsibility to address these crises. The first priority is to win the war against coronavirus. We need to do that while doing all we can to help our stakeholders now and, at the same time, to avoid a prolonged economic impact in the future. We will continue to embody “stakeholder capitalism” and do all we can to help those who are affected, and help secure our common prosperity.
To this end, we endorse the following Stakeholder Principles in the COVID Era:
− To employees, our principle is to keep you safe: We will continue do everything we can to protect your workplace, and to help you to adapt to the new working conditions
− To our ecosystem of suppliers and customers, our principle is to secure our shared business continuity: We will continue to work to keep supply chains open and integrate you into our business response
− To our end consumers, our principle is to maintain fair prices and commercial terms for essential supplies
− To governments and society, our principle is to offer our full support: We stand ready and will continue to complement public action with our resources, capabilities and know-how
− To our shareholders, our principle remains the long-term viability of the company and its potential to create sustained value
Finally, we also maintain the principle that we must continue our sustainability efforts unabated, to bring our world closer to achieving shared goals, including the Paris climate agreement and the United Nations Sustainable Development Agenda. We will continue to focus on those long-term goals.
The world has gone through other crises. As a global community, we will prevail this time as well. But, to do so, we must all bond together and coordinate our response. As business leaders, we pledge to stand at society’s service, to help preserve and rebuild a viable society and economy, and to do all we can for our stakeholders.
À la prochaine…
actualités internationales Gouvernance normes de droit Responsabilité sociale des entreprises Structures juridiques
Public Benefit Corporation : réforme en vue
Ivan Tchotourian 31 juillet 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
En cette période estivale, suivre l’actualité est toujours intéressant. Ma lecture d’un article ce matin « Renewed Interest in IPOs of Public Benefit Corporations » (de Cydney Posner) m’apprenait que l’État américain du Delaware est en train de débattre d’une réforme législative en matière d’entreprise à mission !
Pour accéder à cette réforme : ici
Extrait :
These and other similar risks are some of the reasons that, in adopting laws authorizing PBCs, the Delaware legislature made it particularly difficult to convert a traditional corporation to a PBC. For example, currently, the approval of 2/3 of the outstanding stock is required for a traditional corporation to amend its certificate of incorporation to become a PBC or to merge with another entity if the effect of the merger is to convert the shares into shares of a PBC. (Note that, originally, the vote required for conversion was 90%, which made it well nigh impossible for a traditional public company to convert to a PBC.) Appraisal rights are available to stockholders that did not vote in favor of the conversion or merger. And the same vote is required for conversion from a PBC form of entity into a traditional corporation.
The legislation that was just passed by the House in Delaware would, if ultimately signed into law, eliminate the 2/3 voting requirements, making it easier to convert a traditional corporation to a PBC or a PBC to a traditional corporation. Only the standard stockholder vote provisions would be applicable—generally a vote of a majority of the outstanding shares (or any greater or other vote required under the company’s certificate of incorporation) would be required. The amendments would also eliminate the special appraisal rights provisions, with the result that appraisal rights would not be available for conversions resulting from amendments to the certificate, but standard appraisal rights (§262) would be available in the context of mergers.
In addition, as noted above, the current PBC statute mandates that the board of directors manage the business and affairs of the PBC by balancing “the pecuniary interests of the stockholders, the best interests of those materially affected by the corporation’s conduct, and the specific public benefit or public benefits identified in its certificate of incorporation.” The statute provides that, with respect to a decision implicating the “balance requirement,” directors of PBCs will be deemed to satisfy their fiduciary duties to stockholders and the corporation if their decision “is both informed and disinterested and not such that no person of ordinary, sound judgment would approve.” A PBC is also permitted to include in its certificate, for purposes of its director exculpatory provisions under §102(b)(7) and its indemnification provisions under §145, that any disinterested failure to satisfy the mandate will not be considered to “constitute an act or omission not in good faith, or a breach of the duty of loyalty.”
The new legislation would also amp up the protections for directors of a PBC. The amendments would clarify that a director would not be considered “interested” in connection with a balancing decision solely because of the director’s interest in stock of the corporation, except to the extent that the same ownership would create a conflict of interest if the corporation were not a PBC. The amendments would also provide that, in the absence of a conflict, no failure to satisfy the balancing requirement would, for purposes of §102(b)(7) or §145, be considered “an act or omission not in good faith, or a breach of the duty of loyalty, unless the certificate of incorporation so provides.” That is, the certificate would no longer need to expressly provide for the protection for it to apply. In addition, the amendments would provide that, to bring any lawsuit to enforce the PBC balancing requirement, the plaintiffs must own at least 2% of the corporation’s outstanding shares or, for PBCs listed on a national securities exchange, shares with a market value of at least $2 million, if lower.
À la prochaine…
actualités internationales Gouvernance rémunération
COVID-19 : quel impact sur la rémunération des dirigeants américains ?
Ivan Tchotourian 29 juillet 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
L’Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance publie un bel article sur les conséquences de la COVID-19 sur la rémunération des hauts dirigeants des entreprises américaines : « COVID-19 and Executive Pay: Initial Reactions and Responses« (de Stephen Charlebois, Phillip Pennell, and Rachel Ki).
Extrait :
Though businesses have managed executive pay programs through tough economic conditions before, they now must do so under an unprecedented confluence of external expectations and scrutiny, from the advent of Say on Pay to increased shareholder engagement to the beginning of an era of stakeholder primacy.
While results vary across industries, findings indicate that a majority of U.S. corporations have not yet formulated a response to COVID-19 on executive pay but anticipate taking some form of action later in 2020.
What should you take away from the results of this survey?
- There is no universal response. Findings indicate a variety of approaches influenced by company outlook, industry dynamics and broader context
- That said, most companies are delaying action until there is greater clarity. Companies that already made pay decisions are generally waiting until payout determinations to see if adjustments are necessary, and those that have not yet made decisions in 2020 are delaying until the impact of COVID-19 is better understood
- Companies acting now are doing so out of necessity and are primarily in the hardest-hit industries where immediate cash preservation is a key priority
What are key considerations going forward?
- Timely, effective communication is key. Shareholders, employees and customers are all closely monitoring the actions companies are taking in response to the crisis; if decisions are made, transparent and honest communication can build positive alignment and strengthen relationships with key stakeholders
- Align executive pay with the stakeholder experience. Company actions are being closely monitored and the expectation is that shareholder experience should be reflected in compensation decisions (i.e., significant shareholder value losses or headcount reductions are accompanied by lower pay outcomes for executives)
- Establish objective principles for using discretion. While quantitative metrics may be difficult to rely on at this time, establishing a list of factors for Committees to consider if they decide to apply discretion at the end of the year will allow companies to demonstrate that decisions were made in ways that demonstrably tie back to business context.
À la prochaine…
actualités internationales Gouvernance Normes d'encadrement normes de droit Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
Chaîne d’approvisionnement et RSE : du nouveau en Allemagne
Ivan Tchotourian 15 juillet 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
Selon un article de Les Échos.fr (« L’Allemagne s’attaque à l’éthique de ses entreprises à l’étranger », 15 juillet 2020), Berlin prépare pour la rentrée un projet de loi sur le respect des normes environnementales et sociales sur la chaîne d’approvisionnement des entreprises allemandes.
Extrait :
C’est un jeans bleu produit au Bangladesh, taille haute, banal, mais « il coûte 7 euros aux distributeurs allemands avec toutes les certifications nécessaires sur le respect des droits de l’homme par le producteur. Sans ces normes, il arrive sur le marché allemand à 5 euros : la différence est de 2 euros ». Un pantalon ou des sachets de thé à la main, le ministre allemand du Développement, Gerd Müller, s’est voulu très pédagogue en présentant mardi, à Berlin, les résultats d’une enquête sur le respect des normes sociales et environnementales internationales par les entreprises allemandes.
20 % des entreprises respectent les normes
Selon cette enquête, 98 multinationales allemandes, sur les 455 ayant répondu, respectent leurs engagements, et « c’est déjà une surprise », fait valoir Gerd Müller. « Clairement, l’Allemagne ne peut continuer à traiter la question du respect des normes sociales sur une base volontaire », en conclut Hubertus Heil, le ministre du Travail allemand.
Un cadre général devrait être présenté en août et un projet de loi sur les chaînes d’approvisionnement sera mis sur la table à la rentrée parlementaire, a-t-il annoncé. Son ambition : assurer une gestion des risques « proportionnée et raisonnable » par les entreprises et mettre en place des sanctions avec des amendes ou l’exclusion de marchés publiques à la clef. La loi anticiperait des initiatives européennes annoncées par Bruxelles pour 2021.
À la prochaine…
actualités internationales Gouvernance mission et composition du conseil d'administration normes de droit Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
Grèce : 25 % de femmes au CA imposé par la loi
Ivan Tchotourian 9 juillet 2020
Minerva Analytics apporte une belle mise à jour à la problématique de la diversité en m’apprenant que la Grèce vient de renforcer son dispositif juridique en matière de féminisation : « Greek companies will soon be mandated to meet a 25% female quota on their boards following a landmark decision for gender diversity ».
Extrait :
The quota requirement has been included as an amendment to the bill transposing the EU Shareholder Rights Directive II (SRD II) into Greek law, and is the result of a consultation led by a group of academics specialising in corporate governance.
(…)
Overall, the directive is designed to encourage companies away from short-termism, focusing on areas such as director remuneration. However, the Greek amendment marks the first time it has been used to tackle the EU’s poor record on gender diversity at a board level.
According to the European Commission’s 2019 report on equality between men and women, since 2015, progress on corporate gender inclusivity has stalled. As of October 2018, the proportion of women on the boards of the EU’s biggest companies was only 26.7%.
Within this, France was the only EU member state with at least 40% female representation at board-level, while women account for less than a third of board-level positions in Italy, Sweden, Finland and Germany.
According to the same data, women made up less than 10% of board members in Greece.
À la prochaine…
actualités internationales Divulgation Gouvernance normes de droit
Tranparence en matière de COVID-19 : quel bilan des entreprises aux États-Unis ?
Ivan Tchotourian 9 juillet 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
David Larcker, Bradford Lynch, Brian Tayan et Daniel Taylor publient un texte qui revient sur la transparence des ghrandes entreprises américaines en matière de COVID-19 « The Spread of Covid-19 Disclosure » (29 juin 2020). Un document plein de statistiques et de tendances sur la transparence… vraiment intéressant sachant que l’enjeu de la question n’est pas à négliger.
Extrait :
The COVID-19 pandemic presents an interesting scenario whereby an unexpected shock to the economic system led to a rapid deterioration in the economic landscape, causing sharp changes in performance relative to expectations just a few months prior. For most companies, the pandemic has been detrimental. For a few, it brought unexpected demand. In many cases, supply chains have been strained, causing ripple effects that extend well beyond any one company.
How do companies respond to such a situation? What choices do they make, and how much transparency do they offer? How does disclosure vary in a setting where the potential impact is so widely uncertain? The COVID-19 pandemic provides a unique setting to examine disclosure choices in a situation of extreme uncertainty that extends across all companies in the public market. This devastating outlier event provides a rare glimpse into disclosure behavior by managers and boards.
Why This Matters
- The COVID-19 pandemic provides a unique opportunity to examine disclosure practices of companies relative to peers in real time about a somewhat unprecedented shock that impacted practically every publicly listed company in the U.S. We see that decisions varied considerably about whether to make disclosure and, if so, what and how much to say about the pandemic’s impact on operations, finances, and future. What motivates some companies to be forthcoming about what they are experiencing, while others remain silent? Does this reflect different degrees of certitude about how the virus would impact their businesses, or differences in managements’ perception of their “obligations” to be transparent with the public? What does this say about a company’s view of its relation and duty to shareholders?
- In one example, we saw a consumer beverage company make zero references to COVID-19 in its SEC filings and website, despite the virus plausibly having at least some impact on its business. In another example, we saw a company claim no material changes to its previously reported risk factors when managers almost certainly had relevant information about the virus and the likely impact on sales and operations. What discussion among the senior managers, board members, external auditor, and general counsel leads to a decision to make no disclosures? What should shareholders glean from this decision, particularly in light of peer disclosure?
- The COVID-19 pandemic represents a so-called “black swan” event that inflicted severe and unexpected damage to wide swaths of the economy. What strategic insights will companies learn from this event? Can boards use these insights to prepare for other possible outlier events, such as climate events, terrorism, cyber-attacks, pandemics, and other emergencies? Should these insights be disclosed to shareholders?
À la prochaine…
actualités internationales Gouvernance mission et composition du conseil d'administration
What The Director Of The Future Will Need To Succeed
Ivan Tchotourian 8 juillet 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
Board Member vient de publier une étude sur les CA du futur : « What The Director Of The Future Will Need To Succeed ». Intéressant dans le monde post COVID-19.
Merci à Louise Champoux-Paillé de l’information !
Extrait :
“The future of business will be different,” surmised a director on a recent virtual board roundtable hosted by RSR Partners, “in ways we can’t anticipate in this moment. Our board is focused on assessing whether all our directors are truly ready for what’s coming.”
Over the past few months, RSR Partners hosted more than a dozen roundtables for sitting directors, providing a forum for the participants to share what their boards are learning as they navigate the current crisis and pivot into the “new normal.” While tackling topics as diverse as commercial strategy, operations, health and safety, and the future of business, one theme was pervasive throughout the discussions: leadership and stakeholders will be looking to the boardroom for guidance, and board members not only need to have the requisite experience and skills to confidently provide direction, but the leadership characteristics that will allow them to be effective.
Fundamentally, the global business disruption and current uncertainty has created a need for a higher level of involvement from board members. “This is a time to have board members who have experienced really tough issues, such as major ecessions, difficult mergers, major cost cutting, insolvency and bankruptcy, and top management departures, along with experience in reinventing companies, including supply chain, product engineering and simplification, digital transformation, offshore manufacturing and procurement, sale of subsidiaries, and comprehensive refinancing,” stated Edward A. Kangas, former Chairman and CEO of Deloitte Touche. “This is not a time for deep thinking. It’s time for people with real experience who know how to oversee and support management in a time of crisis and reinvention.” (Mr. Kangas currently serves on the following boards: Deutsche Bank USA Corp., Intelsat SA, VIVUS, Inc., and Hovnanian Enterprises, Inc.).
Characteristics of Directors Who Succeed in the “New Normal”
From a practical perspective, there is now a higher premium placed on a director’s proven ability to navigate a business through a crisis while mitigating risk and understanding how and when to pull the levers that will impact balance sheets. The demand to optimize results, sustain business, and adapt to changes in a regional and global market has increased alongside the time commitment and attention to detail required of directors to address these issues. Normal requirements for sound governance, audit oversight, compensation strategies, business performance goals, and succession of key leadership have continued to be paramount during the crisis. However, what the current crisis has forced boards to recognize is that a combination of specialized and diversified skillsets and characteristics will produce good corporate governance in and after 2020.
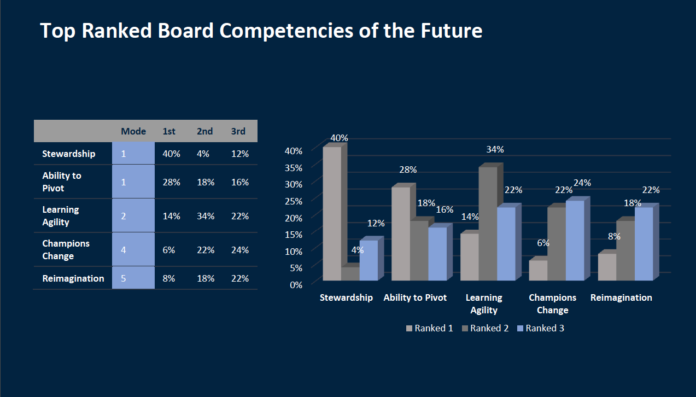
In addition to listening to the characteristics discussed in the recent roundtables, RSR Partners polled more than 250 public company board members of Fortune 50-1000 companies to identify the traits they hope to see emerge in this generation of board members. The results indicated that stewardship, the ability to pivot and learn agility, to be a champion of change, and to be capable of reimagination will be most needed by the directors charged with steering their boards in the “new normal.”
1. Stewardship
2. Ability to Pivot
3. Learning Agility
4. Champions of Change
5. Reimagination
À la prochaine…