Responsabilité sociale des entreprises | Page 2
Divulgation finance sociale et investissement responsable Gouvernance Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
Fonds de pension hollandais : fronde contre le greenwashing
Ivan Tchotourian 23 novembre 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
IPE Magazine de novembre 2020 publie un article de Tjibbe Hoekstra initulé : « Survey: Dutch pension funds accuse asset managers of greenwashing » (16 septembre 2020).
Extrait :
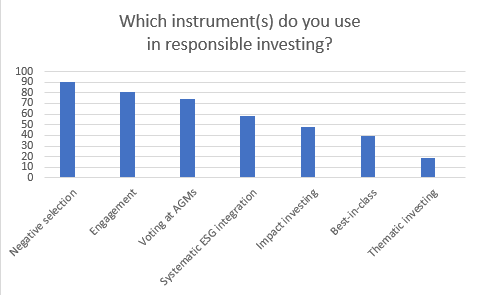
Some asset managers do not invest as responsibly as they claim, a number of Dutch pension funds have said.
In a survey among 31 Dutch pension funds carried out by Dutch pensions publication Pensioen Pro, six in 10 Dutch pension funds agreed with the statement that some asset managers engage in greenwashing.
None of the participating pension funds, with combined assets under management worth €1.2trn, disagreed with the statement that greenwashing is a problem.
An important reason asset managers are being given the chance to engage in greenwashing is a lack of commonly agreed environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) standards, many pension funds believed.
Some 56% of respondents even saw the absence of a common ESG definition as a threat to responsible investing, the survey found.
Responsible investing is a rising trend in the Dutch pension sector, with 87% of the surveyed funds now having their own sustainable investment policy. The remaining 13% have outsourced this to their fiduciary manager.
None of the surveyed funds said they have no dedicated policy for responsible investing.
À la prochaine…
actualités canadiennes Divulgation divulgation extra-financière Normes d'encadrement Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
CFA Institute : document de consultation
Ivan Tchotourian 26 octobre 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
CFA Institute a proposé des standards en matière de divulgation des critères ESG dans les produits financiers : « Consulter Paper on the Development of the CFA Institute – ESG Disclosure Standards For Investments Products » (août 2020).
- Pour un article de presse : ici
Petit extrait :
- Disclosure Requirements Many of the Standard’s requirements will be related to disclosures. Disclosure requirements are a key way to provide transparency and comparability for investors. A disclosure requirement is simply a means of ensuring that asset managers communicate certain information to investors. There are different ways that disclosures might be required, both in terms of scope and method. Therefore, it is necessary to establish principles to ensure the disclosure requirements meet the purpose of the Standard. We propose the following design principles:
- Disclosure requirements should focus on relevant, useful information. Disclosures must provide information that will help investors better understand investment products, make comparisons, and choose among alternatives. • Disclosure requirements should focus primarily on ESG-related features. Because the goal of the Standard is to enable greater transparency and comparability of investment products with ESG-related features, the Standard’s disclosure requirements should focus on these features. Focusing the disclosure requirements on ESG-related features also avoids adding unnecessarily to an asset manager’s disclosure burden.
- Disclosure requirements should allow asset managers the flexibility to make the required disclosure in the clearest possible manner given the nature of the product. Disclosure requirements can easily be reformulated as questions. There are two types of questions—open-ended and closed-ended. Open-ended questions ask who, what, why, where, when, or how. Closed-ended questions require answers in a specific form—either yes/no or selected from a predefined list. The open-ended disclosure requirement format provides the flexibility needed for the Standard to be relevant on a global scale and to pertain to all types of investment products with ESG-related features. The open-ended nature of the disclosure requirements, however, must be balanced to a certain degree with a standardization of responses for the sake of comparison by investors. The forthcoming Exposure Draft will include examples of openended and standardized disclosures.
- The disclosure requirements should aim to elicit a moderate level of detail. An investment product’s disclosures should accurately and adequately represent the policies and procedures that govern the design and implementation of the investment product. The Standard’s disclosure requirements can be thought of as a step between a database search and a due diligence conversation. The disclosures will provide more detail than can be standardized and presented in a database but less detail than the information one can obtain through a full due diligence process.
- The disclosure requirements should prioritize content over format. The disclosure requirements will focus on what information is disclosed rather than how it is disclosed. The Standard will provide a certain degree of flexibility in the format for information presentation. Providing latitude in the format is intended to reduce an asset manager’s disclosure burden and allow for harmonization with disclosures required by regulatory bodies and other standards. The Exposure Draft will offer examples of presentation formats. • Disclosure requirements should be categorized as “general” or “feature-specific”. The Standard will have both general and feature-specific disclosure requirements. General disclosure requirements will apply to all investment products that seek to comply with the Standard. Feature-specific disclosure requirements will apply only to investment products that have a specific ESG-related feature.
- The Standard should include disclosure recommendations in addition to requirements. We anticipate that in addition to the Standard’s required disclosures, the Standard will have recommended disclosures as well. Required disclosures represent the minimum information that must be disclosed in order to comply with the Standard. Recommended disclosures provide additional information that investors may find helpful in their decision making. Recommended disclosures are encouraged but not mandatory.
À la prochaine…
Gouvernance Nouvelles diverses parties prenantes Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
The Stakeholder Model and ESG
Ivan Tchotourian 17 septembre 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
Intéressant article sur l’Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance consacré au modèle partie prenante et à ses liens avec les critères ESG : « The Stakeholder Model and ESG » (Ira Kay, Chris Brindisi et Blaine Martin, 14 septembre 2020).
Extrait :
Is your company ready to set or disclose ESG incentive goals?
ESG incentive metrics are like any other incentive metric: they should support and reinforce strategy rather than lead it. Companies considering ESG incentive metrics should align planning with the company’s social responsibility and environmental strategies, reporting, and goals. Another essential factor in determining readiness is the measurability/quantification of the specific ESG issue.
Companies will generally fall along a spectrum of readiness to consider adopting and disclosing ESG incentive metrics and goals:
- Companies Ready to Set Quantitative ESG Goals: Companies with robust environmental, sustainability, and/or social responsibility strategies including quantifiable metrics and goals (e.g., carbon reduction goals, net zero carbon emissions commitments, Diversity and Inclusion metrics, employee and environmental safety metrics, customer satisfaction, etc.).
- Companies Ready to Set Qualitative Goals: Companies with evolving formalized tracking and reporting but for which ESG matters have been identified as important factors to customers, employees, or other These companies likely already have plans or goals around ESG factors (e.g., LEED [Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design]-certified office space, Diversity and Inclusion initiatives, renewable power and emissions goals, etc.).
- Companies Developing an ESG Strategy: Some companies are at an early stage of developing overall ESG/stakeholder strategies. These companies may be best served to focus on developing a strategy for environmental and social impact before considering linking incentive pay to these priorities.
We note it is critically important that these ESG/stakeholder metrics and goals be chosen and set with rigor in the same manner as financial metrics to ensure that the attainment of the ESG goals will enhance stakeholder value and not serve simply as “window dressing” or “greenwashing.” [9] Implementing ESG metrics is a company-specific design process. For example, some companies may choose to implement qualitative ESG incentive goals even if they have rigorous ESG factor data and reporting.
Will ESG metrics and goals contribute to the company’s value-creation?
The business case for using ESG incentive metrics is to provide line-of-sight for the management team to drive the implementation of initiatives that create significant differentiated value for the company or align with current or emerging stakeholder expectations. Companies must first assess which metrics or initiatives will most benefit the company’s business and for which stakeholders. They must also develop challenging goals for these metrics to increase the likelihood of overall value creation. For example:
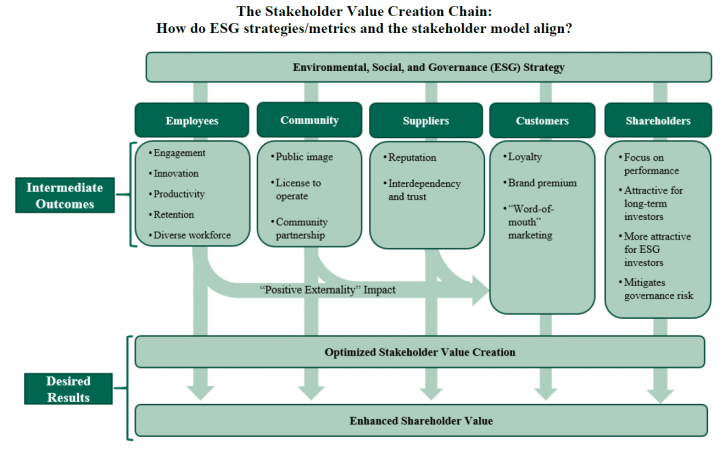
- Employees: Are employees and the competitive talent market driving the need for differentiated environmental or social initiatives? Will initiatives related to overall company sustainability (building sustainability, renewable energy use, net zero carbon emissions) contribute to the company being a “best in class” employer? Diversity and inclusion and pay equity initiatives have company and social benefits, such as ensuring fair and equitable opportunities to participate and thrive in the corporate system.
- Customers: Are customer preferences driving the need to differentiate on sustainable supply chains, social justice initiatives, and/or the product/company’s environmental footprint?
- Long-Term Sustainability: Are long-term macro environmental factors (carbon emissions, carbon intensity of product, etc.) critical to the Company’s ability to operate in the long term?
- Brand Image: Does a company want to be viewed by all constituencies, including those with no direct economic linkage, as a positive social and economic contributor to society?
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to ESG metrics, and companies fall across a spectrum of needs and drivers that affect the type of ESG factors that are relevant to short- and long-term business value depending on scale, industry, and stakeholder drivers. Most companies have addressed, or will need to address, how to implement ESG/stakeholder considerations in their operating strategy.
Conceptual Design Parameters for Structuring Incentive Goals
For those companies moving to implement stakeholder/ESG incentive goals for the first time, the design parameters range widely, which is not different than the design process for implementing any incentive metric. For these companies, considering the following questions can help move the prospect of an ESG incentive metric from an idea to a tangible goal with the potential to create value for the company:
- Quantitative goals versus qualitative milestones. The availability and quality of data from sustainability or social responsibility reports will generally determine whether a company can set a defined quantitative goal. For other companies, lack of available ESG data/goals or the company’s specific pay philosophy may mean ESG initiatives are best measured by setting annual milestones tailored to selected goals.
- Selecting metrics aligned with value creation. Unlike financial metrics, for which robust statistical analyses can help guide the metric selection process (e.g., financial correlation analysis), the link between ESG metrics and company value creation is more nuanced and significantly impacted by industry, operating model, customer and employee perceptions and preferences, etc. Given this, companies should generally apply a principles-based approach to assess the most appropriate metrics for the company as a whole (e.g., assessing significance to the organization, measurability, achievability, etc.) Appendix 1 provides a list of common ESG metrics with illustrative mapping to typical stakeholder impact.
- Determining employee participation. Generally, stakeholder/ESG-focused metrics would be implemented for officer/executive level roles, as this is the employee group that sets company-wide policy impacting the achievement of quantitative ESG goals or qualitative milestones. Alternatively, some companies may choose to implement firm-wide ESG incentive metrics to reinforce the positive employee engagement benefits of the company’s ESG strategy or to drive a whole-team approach to achieving goals.
- Determining the range of metric weightings for stakeholder/ESG goals. Historically, US companies with existing environmental, employee safety, and customer service goals as well as other stakeholder metrics have been concentrated in the extractive, industrial, and utility industries; metric weightings on these goals have ranged from 5% to 20% of annual incentive scorecards. We expect that this weighting range would continue to apply, with the remaining 80%+ of annual incentive weighting focused on financial metrics. Further, we expect that proxy advisors and shareholders may react adversely to non-financial metrics weighted more than 10% to 20% of annual incentive scorecards.
- Considering whether to implement stakeholder/ESG goals in annual versus long-term incentive plans. As noted above, most ESG incentive goals to date have been implemented as weighted metrics in balanced scorecard annual incentive plans for several reasons. However, we have observed increased discussion of whether some goals (particularly greenhouse gas emission goals) may be better suited to long-term incentives. [10] There is no right answer to this question—some milestone and quantitative goals are best set on an annual basis given emerging industry, technology, and company developments; other companies may have a robust long-term plan for which longer-term incentives are a better fit.
- Considering how to operationalize ESG metrics into long-term plans. For companies determining that sustainability or social responsibility goals fit best into the framework of a long-term incentive, those companies will need to consider which vehicles are best to incentivize achievement of strategically important ESG goals. While companies may choose to dedicate a portion of a 3-year performance share unit plan to an ESG metric (e.g., weighting a plan 40% relative total shareholder return [TSR], 40% revenue growth, and 20% greenhouse gas reduction), there may be concerns for shareholders and/or participants in diluting the financial and shareholder-value focus of these incentives. As an alternative, companies could grant performance restricted stock units, vesting at the end of a period of time (e.g., 3 or 4 years) contingent upon achievement of a long-term, rigorous ESG performance milestone. This approach would not “dilute” the percentage of relative TSR and financial-based long-term incentives, which will remain important to shareholders and proxy advisors.
Conclusion
As priorities of stakeholders continue to evolve, and addressing these becomes a strategic imperative, companies may look to include some stakeholder metrics in their compensation programs to emphasize these priorities. As companies and Compensation Committees discuss stakeholder and ESG-focused incentive metrics, each organization must consider its unique industry environment, business model, and cultural context. We interpret the BRT’s updated statement of business purpose as a more nuanced perspective on how to create value for all stakeholders, inclusive of shareholders. While optimizing profits will remain the business purpose of corporations, the BRT’s statement provides support for prioritizing the needs of all stakeholders in driving long-term, sustainable success for the business. For some companies, implementing incentive metrics aligned with this broader context can be an important tool to drive these efforts in both the short and long term. That said, appropriate timing, design, and communication will be critical to ensure effective implementation.
À la prochaine…
engagement et activisme actionnarial finance sociale et investissement responsable Gouvernance mission et composition du conseil d'administration Normes d'encadrement parties prenantes Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
COVID-19, purpose et critères ESG : une alliance nécessaire
Ivan Tchotourian 13 août 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
Billet à découvrir sur le site de Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance pour y lire cet article consacré à la sortie de crise sanitaire et aux apports de la raison d’être et des critères ESG : « ESG and Corporate Purpose in a Disrupted World » (Kristen Sullivan, Amy Silverstein et Leeann Galezio Arthur, 10 août 2020).
Extrait :
Corporate purpose and ESG as tools to reframe pandemic-related disruption
The links between ESG, company strategy, and risk have never been clearer than during the COVID-19 pandemic, when companies have had to quickly pivot and respond to critical risks that previously were not considered likely to occur. The World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Survey 2020, published in January 2020, listed “infectious diseases” as number 10 in terms of potential economic impact, and did not make the top 10 list of risks considered to be “likely.” The impact of the pandemic was further magnified by the disruption it created for the operations of companies and their workforces, which were forced to rethink how and where they did business virtually overnight.
The radical recalibration of risk in the context of a global pandemic further highlights the interrelationships between long-term corporate strategy, the environment, and society. The unlikely scenario of a pandemic causing economic disruption of the magnitude seen today has caused many companies—including companies that have performed well in the pandemic—to reevaluate how they can maintain the long-term sustainability of the enterprise. While the nature and outcomes of that reevaluation will differ based on the unique set of circumstances facing each company, this likely means reframing the company’s role in society and the ways in which it addresses ESG-related challenges, including diversity and inclusion, employee safety, health and well-being, the existence of the physical workplace, supply chain disruptions, and more.
ESG factors are becoming a key determinant of financial strength. Recent research shows that the top 20 percent of ESG-ranked stocks outperformed the US market by over 5 percentage points during a recent period of volatility. Twenty-four out of 26 sustainable index funds outperformed comparable conventional index funds in Q1 2020. In addition, the MSCI ACWI ESG Leaders Index returned 5.24 percent, compared to 4.48 percent for the overall market, since it was established in September 2007 through February 2020. Notably, BlackRock, one of the world’s largest asset managers, recently analyzed the performance of 32 sustainable indices and compared that to their non-sustainable benchmarks as far back as 2015. According to BlackRock the findings indicated that “during market downturns in 2015–16 and 2018, sustainable indices tended to outperform their non-sustainable counterparts.” This trend may be further exacerbated by the effects of the pandemic and the social justice movement.
Financial resilience is certainly not the only benefit. Opportunities for brand differentiation, attraction and retention of top talent, greater innovation, operational efficiency, and an ability to attract capital and increase market valuation are abundant. Companies that have already built ESG strategies, measurements, and high-quality disclosures into their business models are likely to be well-positioned to capitalize on those opportunities and drive long-term value postcrisis.
As businesses begin to reopen and attempt to get back to some sense of normalcy, companies will need to rely on their employees, vendors, and customers to go beyond the respond phase and begin to recover and thrive. In a postpandemic world, this means seeking input from and continuing to build and retain the confidence and trust of those stakeholder groups. Business leaders are recognizing that ESG initiatives, particularly those that prioritize the health and safety of people, will be paramount to recovery.
What are investors and other stakeholders saying?
While current events have forced and will likely continue to force companies to make difficult decisions that may, in the short term, appear to be in conflict with corporate purpose, evidence suggests that as companies emerge from the crisis, they will refresh and recommit to corporate purpose, using it as a compass to focus ESG performance. Specific to the pandemic, the public may expect that companies will continue to play a greater role in helping not only employees, but the nation in general, through such activities as manufacturing personal protective equipment (PPE), equipment needed to treat COVID-19 patients, and retooling factories to produce ventilators, hand sanitizer, masks, and other items needed to address the pandemic. In some cases, decisions may be based upon or consistent with ESG priorities, such as decisions regarding employee health and well-being. From firms extending paid sick leave to all employees, including temporary workers, vendors, and contract workers, to reorienting relief funds to assist vulnerable populations, examples abound of companies demonstrating commitments to people and communities. As companies emerge from crisis mode, many are signaling that they will continue to keep these principles top of mind. This greater role is arguably becoming part of the “corporate social contract” that legitimizes and supports the existence and prosperity of corporations.
In the United States, much of the current focus on corporate purpose and ESG is likely to continue to be driven by investors rather than regulators or legislators in the near term. Thus, it’s important to consider investors’ views, which are still developing in the wake of COVID-19 and other developments.
Investors have indicated that they will assess a company’s response to the pandemic as a measure of stability, resilience ,and adaptability. Many have stated that employee health, well-being, and proactive human capital management are central to business continuity. Investor expectations remain high for companies to lead with purpose, particularly during times of severe economic disruption, and to continue to demonstrate progress against ESG goals.
State Street Global Advisors president and CEO Cyrus Taraporevala, in a March 2020 letter to board members, emphasized that companies should not sacrifice the long-term health and sustainability of the company when responding to the pandemic. According to Taraporevala, State Street continues “to believe that material ESG issues must be part of the bigger picture and clearly articulated as part of your company’s overall business strategy.” According to a recent BlackRock report, “companies with strong profiles on material sustainability issues have potential to outperform those with poor profiles. We believe companies managed with a focus on sustainability may be better positioned versus their less sustainable peers to weather adverse conditions while still benefiting from positive market environments.”
In addition to COVID-19, the recent social justice movement compels companies to think holistically about their purpose and role in society. Recent widespread protests of systemic, societal inequality leading to civil unrest and instability elevate the conversation on the “S” and “G” in ESG. Commitments to the health and well-being of employees, customers, communities, and other stakeholder groups will also require corporate leaders to address how the company articulates its purpose and ESG objectives through actions that proactively address racism and discrimination in the workplace and the communities where they operate. Companies are responding with, among other things, statements of support for diversity and inclusion efforts, reflective conversations with employees and customers, and monetary donations for diversity-focused initiatives. However, investors and others who are pledging to use their influence to hold companies accountable for meaningful progress on systemic inequality will likely look for data on hiring practices, pay equity, and diversity in executive management and on the board as metrics for further engagement on this issue.
What can boards do?
Deloitte US executive chair of the board, Janet Foutty, recently described the board as “the vehicle to hold an organization to its societal purpose.” Directors play a pivotal role in guiding
companies to balance short-term decisions with long-term strategy and thus must weigh the needs of all stakeholders while remaining cognizant of the risks associated with each decision. COVID-19 has underscored the role of ESG principles as central to business risk and strategy, as well as building credibility and trust with investors and the public at large. Boards can advise management on making clear, stakeholder-informed decisions that position the organization to emerge faster and stronger from a crisis.
It has been said before that those companies that do not control their own ESG strategies and narratives risk someone else controlling their ESG story. This is particularly true with regards to how an organization articulates its purpose and stays grounded in that purpose and ESG principles during a crisis. Transparent, high-quality ESG disclosure can be a tool to provide investors with information to efficiently allocate capital for long-term return. Boards have a role in the oversight of both the articulation of the company’s purpose and how those principles are integrated with strategy and risk.
As ESG moves to the top of the board agenda, it is important for boards to have the conversation on how they define the governance structure they will put in place to oversee ESG. Based on a recent review, completed by Deloitte’s Center for Board Effectiveness, of 310 company proxies in the S&P 500, filed from September 1, 2019, through May 6, 2020, 57 percent of the 310 companies noted that the nominating or governance committee has primary oversight responsibility, and only 9 percent noted the full board, with the remaining 34 percent spread across other committees. Regardless of the primary owner, the audit committee should be engaged with regard to any ESG disclosures, as well as prepared to oversee assurance associated with ESG metrics.
Conclusion
The board’s role necessitates oversight of corporate purpose and how corporate purpose is executed through ESG. Although companies will face tough decisions, proactive oversight of and transparency around ESG can help companies emerge from recent events with greater resilience and increased credibility. Those that have already embarked on this journey and stay the course will likely be those well-positioned to thrive in the future.
Questions for the board to consider asking:
How are the company’s corporate purpose and ESG objectives integrated with strategy and risk?
- Has management provided key information and assumptions about how ESG is addressed during the strategic planning process?
- How is the company communicating its purpose and ESG objectives to its stakeholders?
- What data does the company collect to assess the impact of ESG performance on economic performance, how does this data inform internal management decision- making, and how is the board made aware of and involved from a governance perspective?
- Does the company’s governance structure facilitate effective oversight of the company’s ESG matters?
- How is the company remaining true to its purpose and ESG, especially now given COVID-19 pandemic and social justice issues?
- What is the board’s diversity profile? Does the board incorporate diversity when searching for new candidates?
- Have the board and management discussed executive management succession and how the company can build a diverse pipeline of candidates?
- How will the company continue to refresh and recommit to its corporate purpose and ESG objectives as it emerges from the pandemic response and recovery and commit to accelerating diversity and inclusion efforts?
- How does the company align its performance incentives for executive leadership with attaining critical ESG goals and outcomes?
À la prochaine…
actualités internationales Divulgation divulgation extra-financière Gouvernance Normes d'encadrement normes de droit normes de marché Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
Approche juridique sur la transparence ESG
Ivan Tchotourian 3 août 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
Excellente lecture ce matin de ce billet du Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance : « Legal Liability for ESG Disclosures » (de Connor Kuratek, Joseph A. Hall et Betty M. Huber, 3 août 2020). Dans cette publication, vous trouverez non seulement une belle synthèse des référentiels actuels, mais aussi une réflexion sur les conséquences attachées à la mauvaise divulgation d »information.
Extrait :
3. Legal Liability Considerations
Notwithstanding the SEC’s position that it will not—at this time—mandate additional climate or ESG disclosure, companies must still be mindful of the potential legal risks and litigation costs that may be associated with making these disclosures voluntarily. Although the federal securities laws generally do not require the disclosure of ESG data except in limited instances, potential liability may arise from making ESG-related disclosures that are materially misleading or false. In addition, the anti-fraud provisions of the federal securities laws apply not only to SEC filings, but also extend to less formal communications such as citizenship reports, press releases and websites. Lastly, in addition to potential liability stemming from federal securities laws, potential liability could arise from other statutes and regulations, such as federal and state consumer protection laws.
A. Federal Securities Laws
When they arise, claims relating to a company’s ESG disclosure are generally brought under Section 11 of the Securities Act of 1933, which covers material misstatements and omissions in securities offering documents, and under Section 10(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and rule 10b-5, the principal anti-fraud provisions. To date, claims brought under these two provisions have been largely unsuccessful. Cases that have survived the motion to dismiss include statements relating to cybersecurity (which many commentators view as falling under the “S” or “G” of ESG), an oil company’s safety measures, mine safety and internal financial integrity controls found in the company’s sustainability report, website, SEC filings and/or investor presentations.
Interestingly, courts have also found in favor of plaintiffs alleging rule 10b-5 violations for statements made in a company’s code of conduct. Complaints, many of which have been brought in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York, have included allegations that a company’s code of conduct falsely represented company standards or that public comments made by the company about the code misleadingly publicized the quality of ethical controls. In some circumstances, courts found that statements about or within such codes were more than merely aspirational and did not constitute inactionable puffery, including when viewed in context rather than in isolation. In late March 2020, for example, a company settled a securities class action for $240 million alleging that statements in its code of conduct and code of ethics were false or misleading. The facts of this case were unusual, but it is likely that securities plaintiffs will seek to leverage rulings from the court in that class action to pursue other cases involving code of conducts or ethics. It remains to be seen whether any of these code of conduct case holdings may in the future be extended to apply to cases alleging 10b-5 violations for statements made in a company’s ESG reports.
B. State Consumer Protection Laws
Claims under U.S. state consumer protection laws have been of limited success. Nevertheless, many cases have been appealed which has resulted in additional litigation costs in circumstances where these costs were already significant even when not appealed. Recent claims that were appealed, even if ultimately failed, and which survived the motion to dismiss stage, include claims brought under California’s consumer protection laws alleging that human right commitments on a company website imposed on such company a duty to disclose on its labels that it or its supply chain could be employing child and/or forced labor. Cases have also been dismissed for lack of causal connection between alleged violation and economic injury including a claim under California, Florida and Texas consumer protection statutes alleging that the operator of several theme parks failed to disclose material facts about its treatment of orcas. The case was appealed to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, but was dismissed for failure to show a causal connection between the alleged violation and the plaintiffs’ economic injury.
Overall, successful litigation relating to ESG disclosures is still very much a rare occurrence. However, this does not mean that companies are therefore insulated from litigation risk. Although perhaps not ultimately successful, merely having a claim initiated against a company can have serious reputational damage and may cause a company to incur significant litigation and public relations costs. The next section outlines three key takeaways and related best practices aimed to reduce such risks.
C. Practical Recommendations
Although the above makes clear that ESG litigation to date is often unsuccessful, companies should still be wary of the significant impacts of such litigation. The following outlines some key takeaways and best practices for companies seeking to continue ESG disclosure while simultaneously limiting litigation risk.
Key Takeaway 1: Disclaimers are Critical
As more and more companies publish reports on ESG performance, like disclaimers on forward-looking statements in SEC filings, companies are beginning to include disclaimers in their ESG reports, which disclaimers may or may not provide protection against potential litigation risks. In many cases, the language found in ESG reports will mirror language in SEC filings, though some companies have begun to tailor them specifically to the content of their ESG reports.
From our limited survey of companies across four industries that receive significant pressure to publish such reports—Banking, Chemicals, Oil & Gas and Utilities & Power—the following preliminary conclusions were drawn:
- All companies surveyed across all sectors have some type of “forward-looking statement” disclaimer in their SEC filings; however, these were generic disclaimers that were not tailored to ESG-specific facts and topics or relating to items discussed in their ESG reports.
- Most companies had some sort of disclaimer in their Sustainability Report, although some were lacking one altogether. Very few companies had disclaimers that were tailored to the specific facts and topics discussed in their ESG reports:
- In the Oil & Gas industry, one company surveyed had a tailored ESG disclaimer in its ESG Report; all others had either the same disclaimer as in SEC filings or a shortened version that was generally very broad.
- In the Banking industry, two companies lacked disclaimers altogether, but the rest had either their SEC disclaimer or a shortened version.
- In the Utilities & Power industry, one company had no disclaimer, but the rest had general disclaimers.
- In the Chemicals industry, three companies had no disclaimer in their reports, but the rest had shortened general disclaimers.
- There seems to be a disconnect between the disclaimers being used in SEC filings and those found in ESG In particular, ESG disclaimers are generally shorter and will often reference more detailed disclaimers found in SEC filings.
Best Practices: When drafting ESG disclaimers, companies should:
- Draft ESG disclaimers carefully. ESG disclaimers should be drafted in a way that explicitly covers ESG data so as to reduce the risk of litigation.
- State that ESG data is non-GAAP. ESG data is usually non-GAAP and non-audited; this should be made clear in any ESG Disclaimer.
- Have consistent disclaimers. Although disclaimers in SEC filings appear to be more detailed, disclaimers across all company documents that reference ESG data should specifically address these issues. As more companies start incorporating ESG into their proxies and other SEC filings, it is important that all language follows through.
Key Takeaway 2: ESG Reporting Can Pose Risks to a Company
This article highlighted the clear risks associated with inattentive ESG disclosure: potential litigation; bad publicity; and significant costs, among other things.
Best Practices: Companies should ensure statements in ESG reports are supported by fact or data and should limit overly aspirational statements. Representations made in ESG Reports may become actionable, so companies should disclose only what is accurate and relevant to the company.
Striking the right balance may be difficult; many companies will under-disclose, while others may over-disclose. Companies should therefore only disclose what is accurate and relevant to the company. The US Chamber of Commerce, in their ESG Reporting Best Practices, suggests things in a similar vein: do not include ESG metrics into SEC filings; only disclose what is useful to the intended audience and ensure that ESG reports are subject to a “rigorous internal review process to ensure accuracy and completeness.”
Key Takeaway 3: ESG Reporting Can Also be Beneficial for Companies
The threat of potential litigation should not dissuade companies from disclosing sustainability frameworks and metrics. Not only are companies facing investor pressure to disclose ESG metrics, but such disclosure may also incentivize companies to improve internal risk management policies, internal and external decisional-making capabilities and may increase legal and protection when there is a duty to disclose. Moreover, as ESG investing becomes increasingly popular, it is important for companies to be aware that robust ESG reporting, which in turn may lead to stronger ESG ratings, can be useful in attracting potential investors.
Best Practices: Companies should try to understand key ESG rating and reporting methodologies and how they match their company profile.
The growing interest in ESG metrics has meant that the number of ESG raters has grown exponentially, making it difficult for many companies to understand how each “rater” calculates a company’s ESG score. Resources such as the Better Alignment Project run by the Corporate Reporting Dialogue, strive to better align corporate reporting requirements and can give companies an idea of how frameworks such as CDP, CDSB, GRI and SASB overlap. By understanding the current ESG market raters and methodologies, companies will be able to better align their ESG disclosures with them. The U.S. Chamber of Commerce report noted above also suggests that companies should “engage with their peers and investors to shape ESG disclosure frameworks and standards that are fit for their purpose.”
À la prochaine…
finance sociale et investissement responsable Normes d'encadrement normes de marché Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
Placement ESG : un rappel judicieux
Ivan Tchotourian 29 juillet 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
Intéressant article dans Le Temps consacré à la financiarisation de la RSE : « Les placements ESG allient recherche du profit et valeurs individuelles » (6 juillet 2020). Une belle synthèse !
Extrait :
En 2019, selon l’association sectorielle Swiss Sustainable Finance, quelque 1163 milliards de francs ont été investis de façon durable en Suisse, soit une hausse de 62% par rapport à l’année précédente. Cela démontre que les investisseurs actuels se soucient de savoir où va leur argent. Ils aspirent à générer des rendements solides avec leur patrimoine tout en assumant leur responsabilité sociale et en contribuant ainsi à rendre notre monde un peu meilleur.
L’une des options pour y parvenir réside dans les placements durables, associés fréquemment aux trois lettres E, S et G, soit ESG. A cet égard, les entreprises dans lesquelles il s’agit d’investir sont passées au peigne fin. Qu’en est-il du facteur E comme «environnement»? Comment abordent-elles concrètement les questions écologiques? Comment gèrent-elles le S, à savoir les aspects sociaux, à l’interne comme à l’extérieur? Et à quoi ressemble le G comme «gouvernance», soit la gestion de l’entreprise?
Par le biais de critères fondés scientifiquement, il est possible de mesurer et d’évaluer les performances correspondantes des entreprises. Les investisseurs peuvent ainsi savoir si leurs investissements sont en adéquation avec leurs valeurs personnelles et s’ils ont un impact positif, notamment en fonction des 17 Objectifs de développement durable de l’ONU (ODD). C’est précisément parce que les placements durables responsabilisent les entreprises qu’ils fournissent une importante contribution à l’atteinte desdits objectifs.
(…) Ce dernier a d’ailleurs encore gagné en importance en raison de la pandémie de Covid-19. Actuellement, les Etats encouragent assidûment la recherche d’un vaccin. Auprès des investisseurs, les placements durables connaissent précisément un essor sans précédent. Karsten Güttler, Senior Sustainable Investment Specialist chez UBS Asset Management: «Durant le premier trimestre de cette année, les fonds à orientation durable ont attiré un niveau record de capitaux sur les marchés mondiaux, même lorsque ceux-ci se trouvaient sous le joug de la pandémie. Les fonds durables mondiaux ont connu un afflux de quelque 50 milliards de dollars, tandis que, selon Morningstar, l’univers de fonds plus large a enregistré un assèchement de l’ordre de 400 milliards de dollars.»
Cette tendance est due à deux facteurs: «Les données du marché illustrent que les indices ESG tels que le MSCI SRI global et l’ACWI ont réalisé des rendements ajustés au risque supérieurs à ceux de leurs pendants traditionnels sur trois et cinq ans», explique Karsten Güttler. Il est également possible de mieux exploiter les opportunités à long terme, notamment en misant sur des placements durables ou des investissements liés aux 17 Objectifs de développement durable. «Si l’on saute dans le train à temps, on a des chances de réaliser des bénéfices. Davantage que dans les secteurs en stagnation à faible potentiel de croissance.» En associant croissance et durabilité, on crée une plus-value pour les investisseurs comme pour la société dans son ensemble.
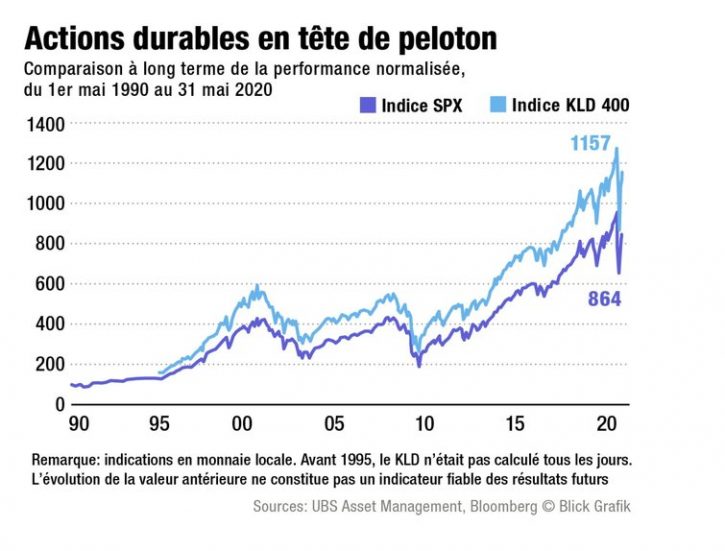
L’excellente rentabilité des placements durables est illustrée par la comparaison de l’indice S&P 500, qui regroupe les actions des 500 principales entreprises américaines cotées en bourse, et du KLD 400. Le KLD 400 reflète le développement des entreprises américaines présentant un meilleur profil ESG. Karsten Güttler: «Le KLD 400 l’emporte haut la main, comme en témoigne l’analyse de 1990 à nos jours. Et cela était déjà le cas bien avant que la thématique ne devienne monnaie courante.» Le KLD 400 englobe environ 250 actions du S&P 500, une centaine d’autres entreprises importantes non listées dans le S&P 500, ainsi qu’environ 50 sociétés qui se distinguent par un profil social soutenu.
Pour les investisseurs, il n’a donc jamais été plus judicieux de placer leur argent durablement et d’intégrer ce faisant les critères ESG dans le processus de décision. Attention toutefois: miser exclusivement sur des entreprises au bilan ESG favorable ne suffit pas. «Investissez également dans les changements positifs en matière de développement durable, conseille Karsten Güttler. Même si cela paraître illogique de prime abord, vous bénéficiez ainsi d’un outil performant attrayant financièrement et qui réalise une plus-value sociale maximale, étant donné qu’il intègre l’ensemble des sujets économiques.»
Autre facteur important: en tant qu’individu, on ne peut pas déplacer des montagnes avec son droit de vote. En investissant dans un fonds, en revanche, toutes les forces sont concentrées et s’érigent tel un puissant glaive des investisseurs. «Cela fait la différence.»
À la prochaine…
Divulgation Gouvernance mission et composition du conseil d'administration Responsabilité sociale des entreprises
Et le « E » des ESG ?
Ivan Tchotourian 9 juillet 2020 Ivan Tchotourian
Voilà une belle question abordée dans ce billet du Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance « What Board Members Need to Know about the “E” in ESG » (par Sheila M. Harvey, Reza S. Zarghamee et Jonathan M. Ocker, 9 juillet 2020) !
Extrait concernant les CA :
Board Responsibilities
Traditionally, a company’s board will manage corporate governance risks and executive compensation. The practical need to expand these responsibilities to account for environmental stewardship and risk management is a relatively new phenomenon, and many boards are not yet up to speed.
The first step toward properly addressing environmental matters is for the board to collaborate with management to identify the different ways in which the company’s businesses and operations interface with environmental issues. The aim here is to think expansively. For purposes of ESG, environmental matters extend beyond regulatory compliance and impacts on natural resources to include concepts such as environmental justice, carbon footprints, supply chains and product stewardship.
Consistent with this approach, an equally broad realm of potential environmental risks also should be considered. These may include the potential to cause environmental contamination and natural resource damages, which may trigger not just cleanup liabilities but also disclosure requirements in financial statements. Also relevant is the potential for business operations to be disrupted by environmental factors such as climate change.
Once potential environmental risks are identified, assessments should be made regarding their materiality and the existence of standing corporate policies and procedures to address them. Where such policies are lacking, they should be developed and implemented. Moreover, determinations should be made about how the company will present itself to investors, regulators and society to adequately inform them of potential environmental risks, avoid reputational harm and increase long-term value.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution, and companies have different environmental profiles. Each will have to find its own way, but the board should make sure that management devotes the appropriate resources to addressing environmental matters, understands environmental disclosure requirements and standards and ranking systems, and takes a proactive approach to protecting the company’s reputation from an environmental standpoint.
This is a multifaceted paradigm that requires open lines of communication between management and the board at all times. Moreover, because not every board member can be an ESG expert, we recommend that the appropriate committee be tasked in its charter with spearheading the environmental risk area for the board.
Points à retenir :
- Corporate boards should partner with management to ensure appropriate and regular oversight of environmental issues critical to the long-term economic success and reputation of the company.
- Either the board or an authorized committee should receive briefings on environmental matters/risks that may jeopardize a company’s reputation and corrective action undertaken to address those risks.
- Management should monitor environmental disclosures and rankings of peer firms and consult with the board on how to improve their company’s standing relative to competing firms and in terms of stakeholder expectations.
À la prochaine…